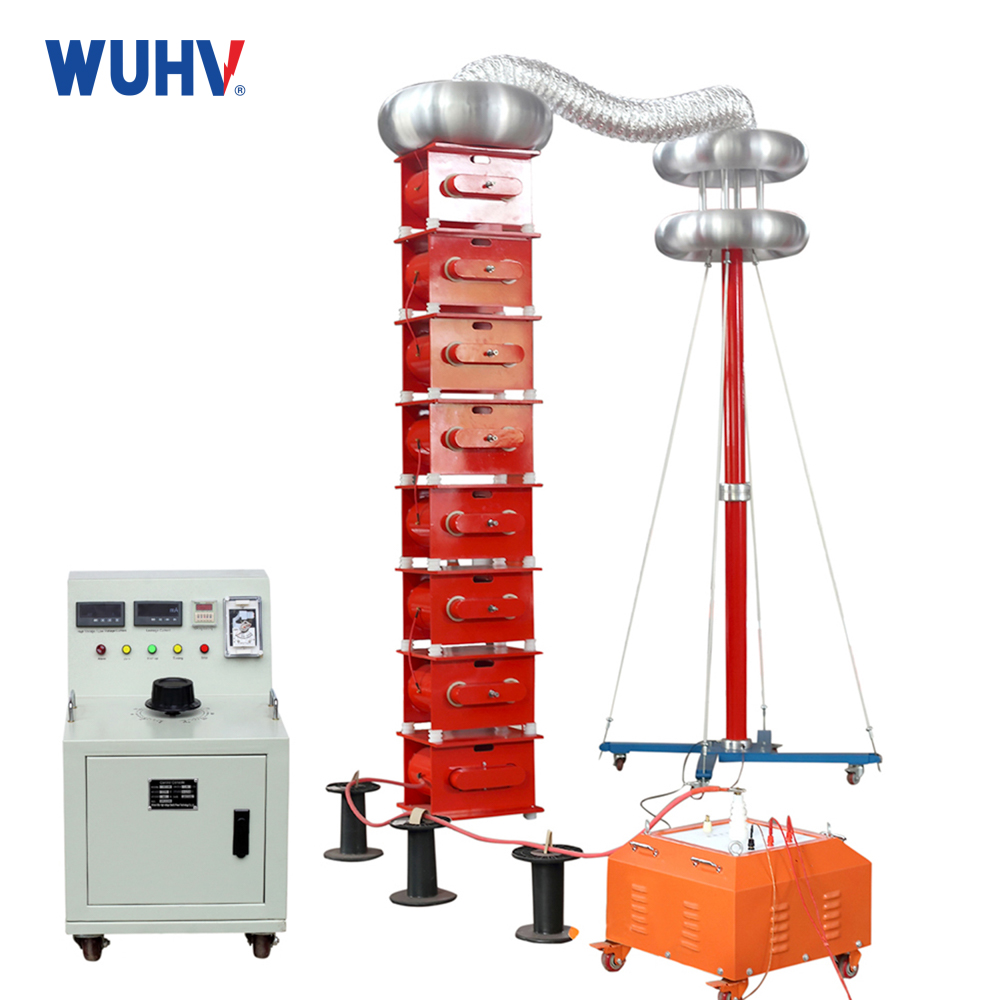
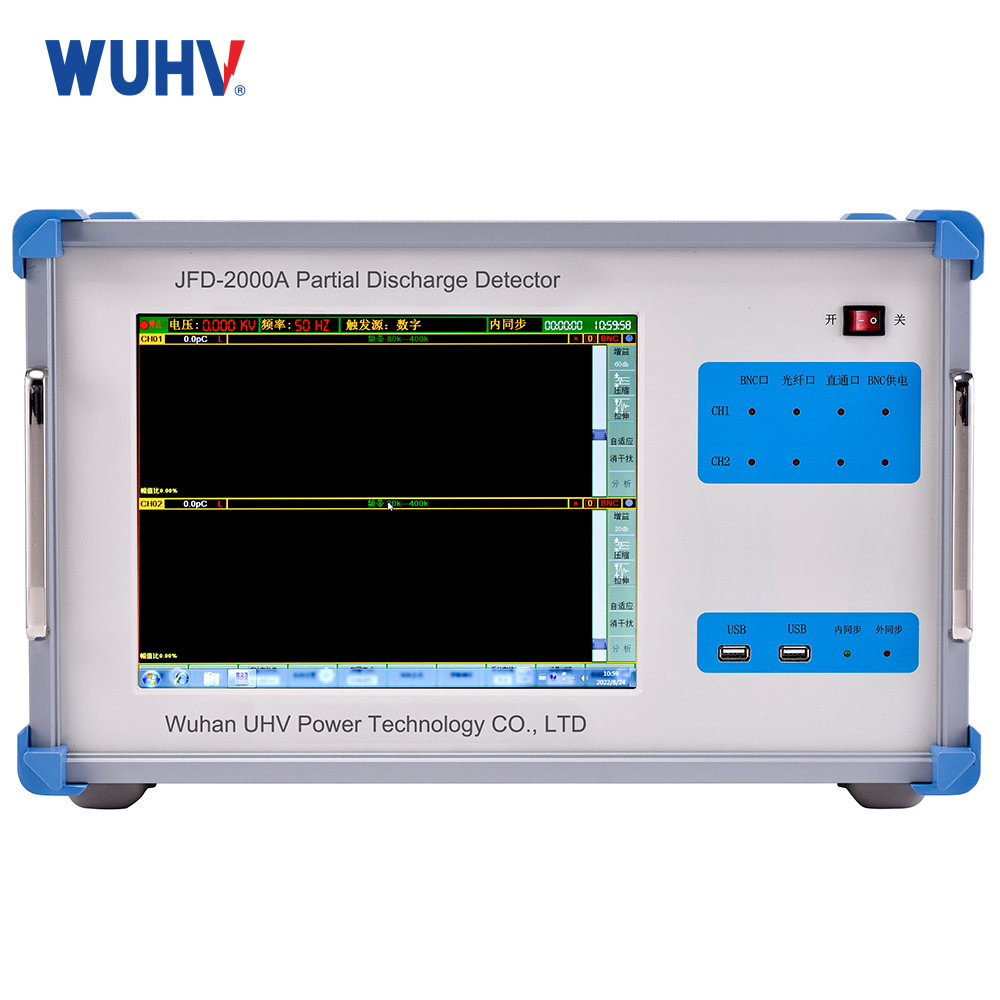
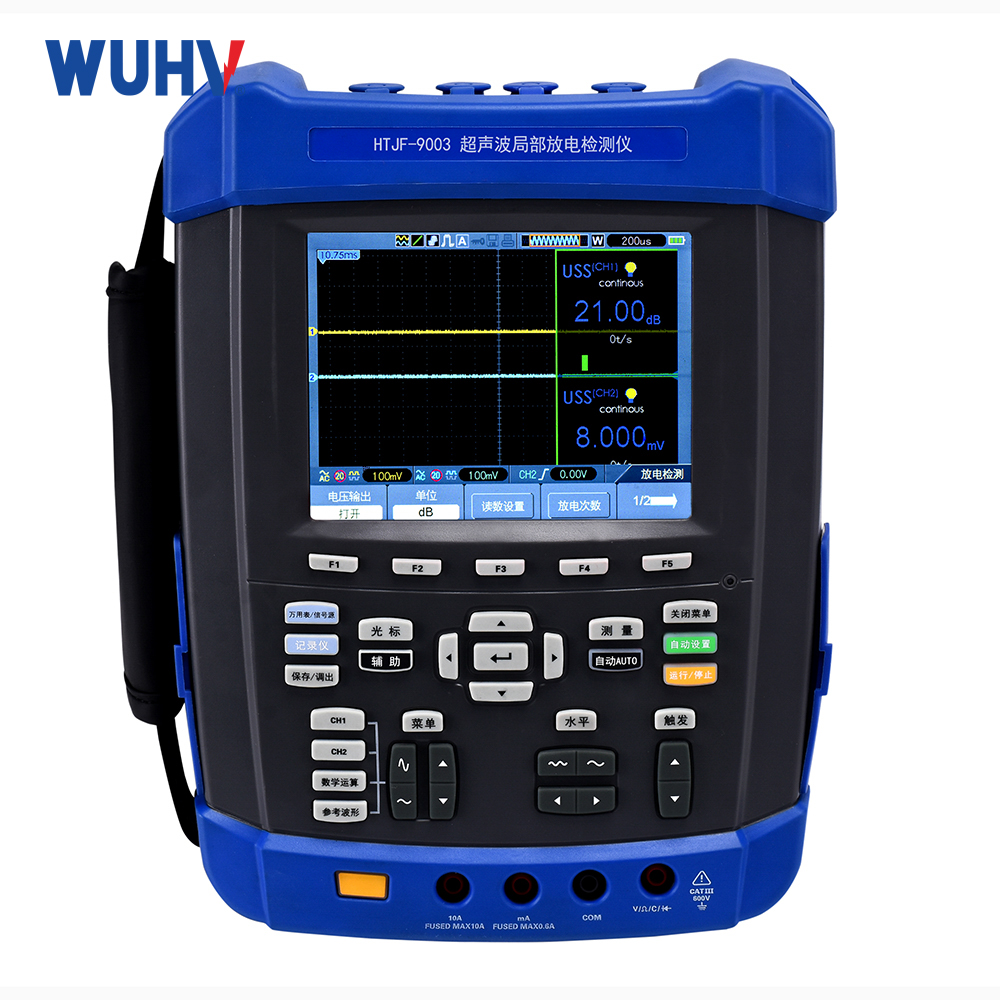
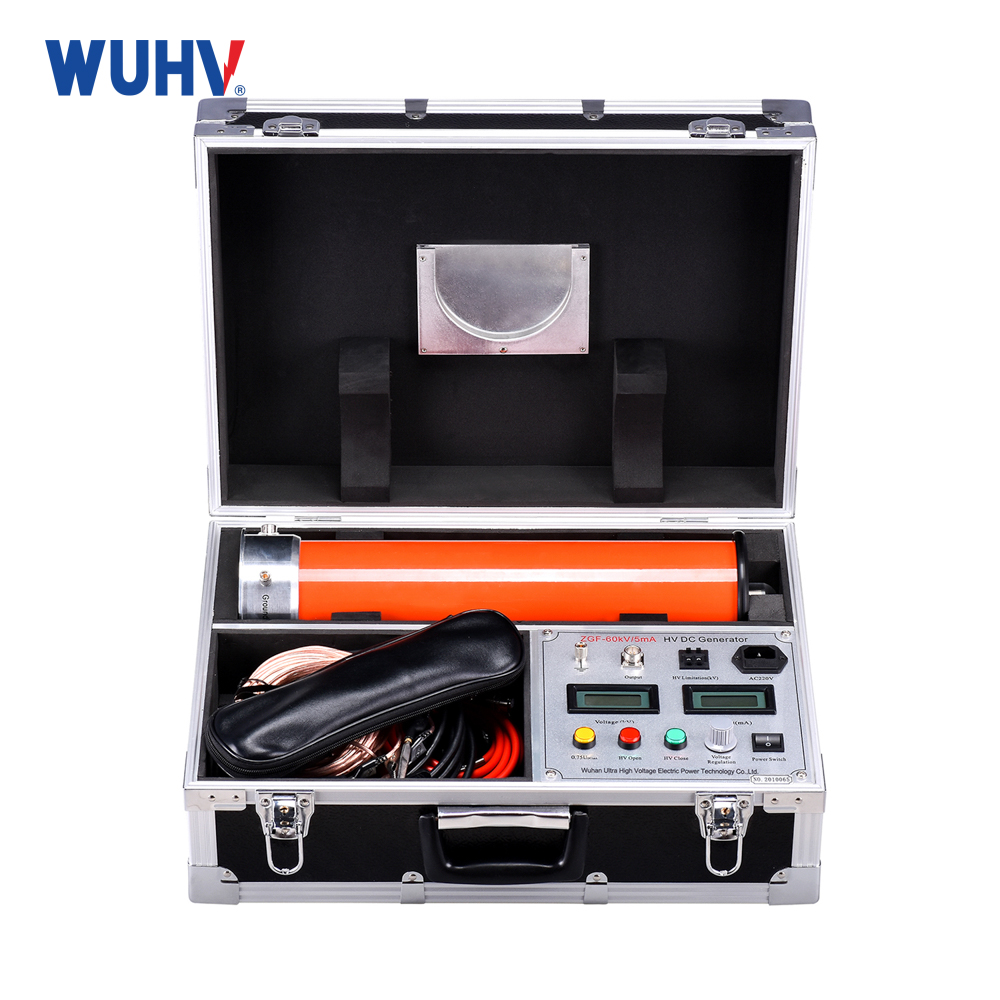
The DC hipot testerunder Wuhan UHV can help many power workers conduct various power tests more conveniently.
1.Applied Voltage:
AC Test: Applies power-frequency (50/60Hz) sinusoidal AC voltage.
DC Test: Applies constant or slowly rising DC voltage.
2.Simulates Real Operation:
AC Test: Most accurately simulates the AC voltage stress equipment experiences during actual operation. It's the gold standard for AC equipment insulation strength assessment.
DC Test: Primarily simulates stress for DC equipment or serves as a supplementary test for AC equipment.
3.Primary Applications:
AC Test: Widely used for most AC power equipment (transformers, GIS, circuit breakers, instrument transformers, generator stators).
DC Test: Particularly suited for long power cables and generator rotor windings; also used for leakage current measurement on some HV equipment (e.g., bushings, arresters).
4.Defect Detection Focus:
AC Test: Highly sensitive to overall insulation degradation, partial discharges (caused by voids, delamination), and surface discharges. Tends to cause complete breakdown at defect sites.
DC Test: Highly sensitive to concentrated through-defects (cracks, penetrating moisture/contamination). Measures leakage current and its change (e.g., absorption ratio) to assess insulation condition. Less sensitive to partial discharges and distributed defects (like uniform moisture). Generally causes less insulation damage.
5.Equipment Requirements:
AC Test: Requires high-capacity test transformers (to supply capacitive charging current), making equipment bulky and expensive.
DC Test: Only needs to supply small leakage current, requiring low-capacity, lightweight, portable equipment – ideal for field use (e.g., cable testing).
6.Voltage Distribution in Insulation:
AC Test: Voltage distributes according to capacitance (capacitive).
DC Test: Voltage distributes according to resistance (resistive).
7.Equivalence for AC Equipment:
The AC Test directly equates to actual AC operational stress.
The DC Test is not fully equivalent to AC operation. DC test voltages are typically set much higher (e.g., 2-4 times) than AC test voltages to achieve equivalent severity.
Summary & Selection:
AC Withstand Test is the primary and preferred method for qualifying insulation strength in AC equipment (often mandated by standards).
DC Withstand Test is the main method for cables (especially long ones) and rotor windings, and a valuable supplementary method for leakage current measurement on AC equipment (due to portability). Important Note: For XLPE cables, DC testing may cause damage; AC testing methods (like Variable Frequency Resonant or 0.1Hz Very Low Frequency - VLF) are increasingly recommended/preferred.
Always follow the specific standards applicable to the equipment being tested.