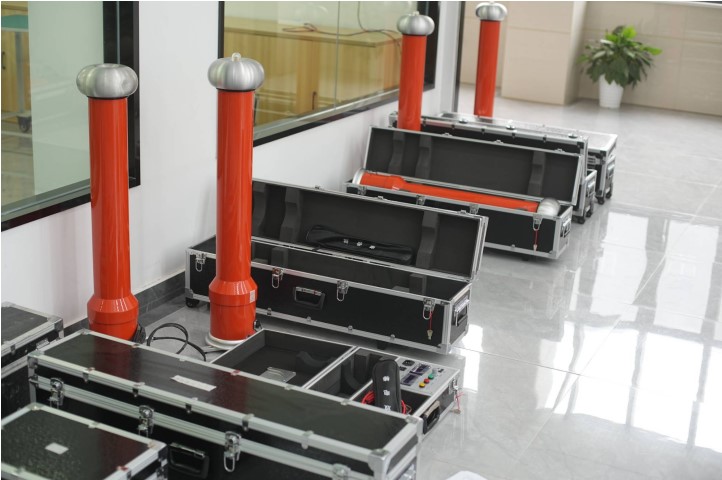
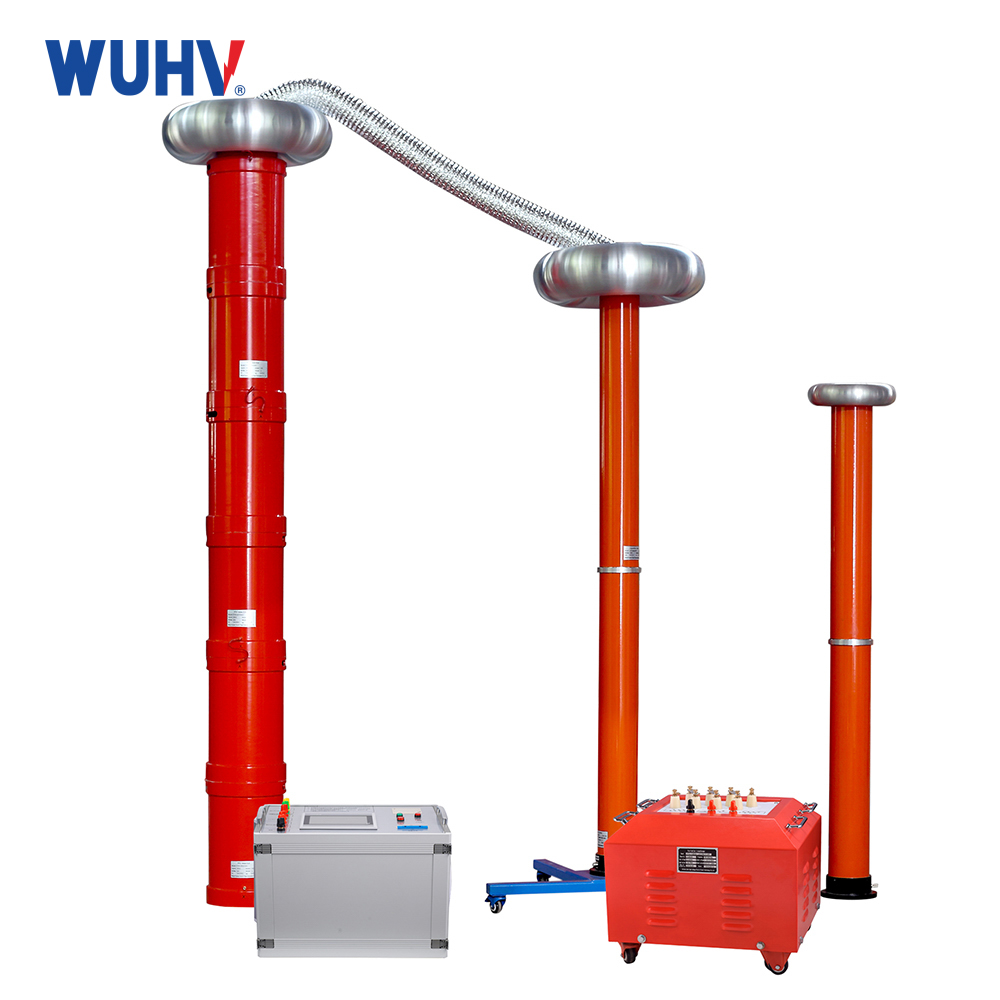
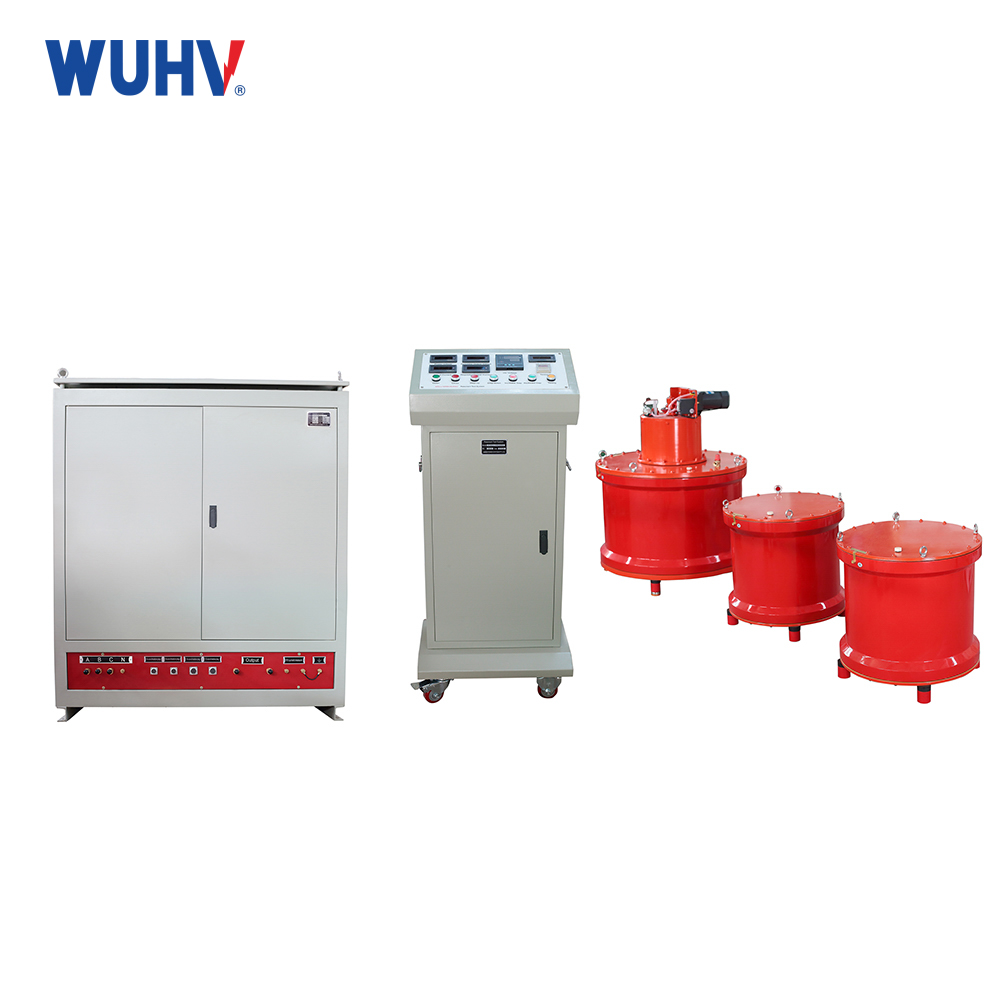
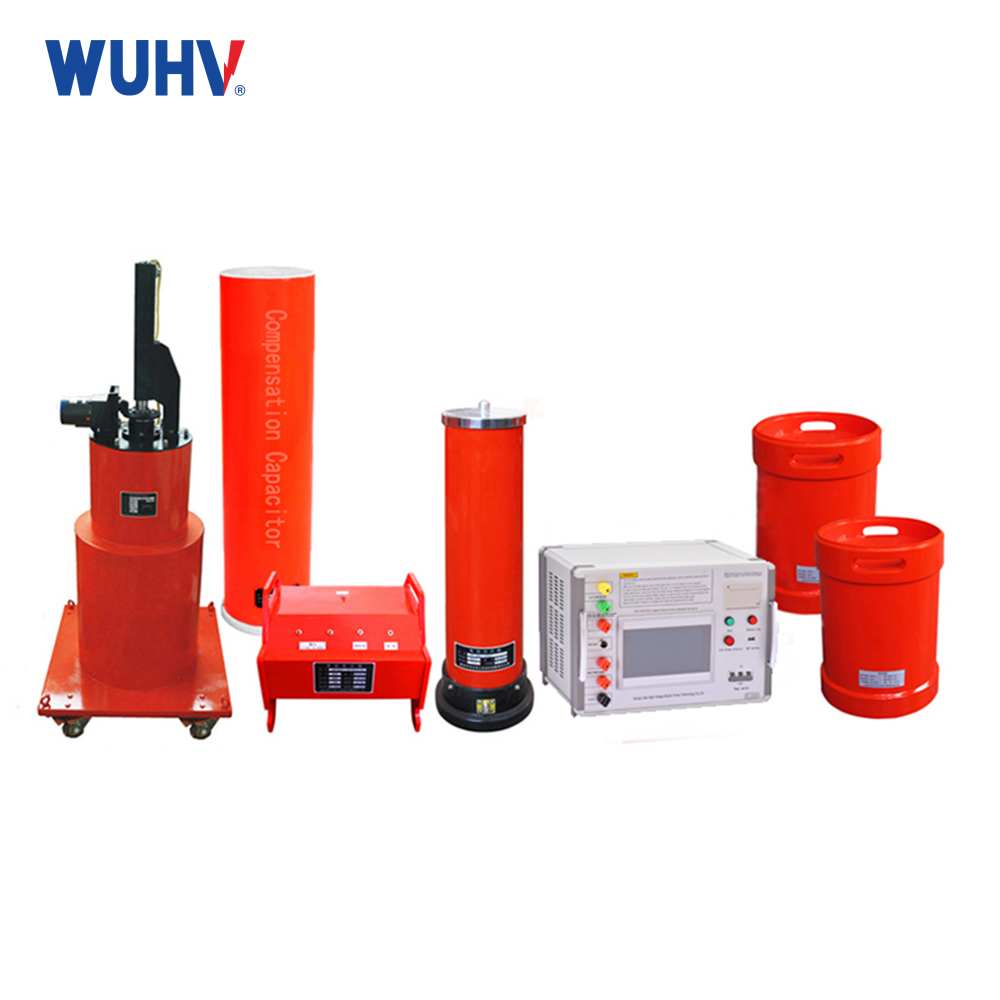
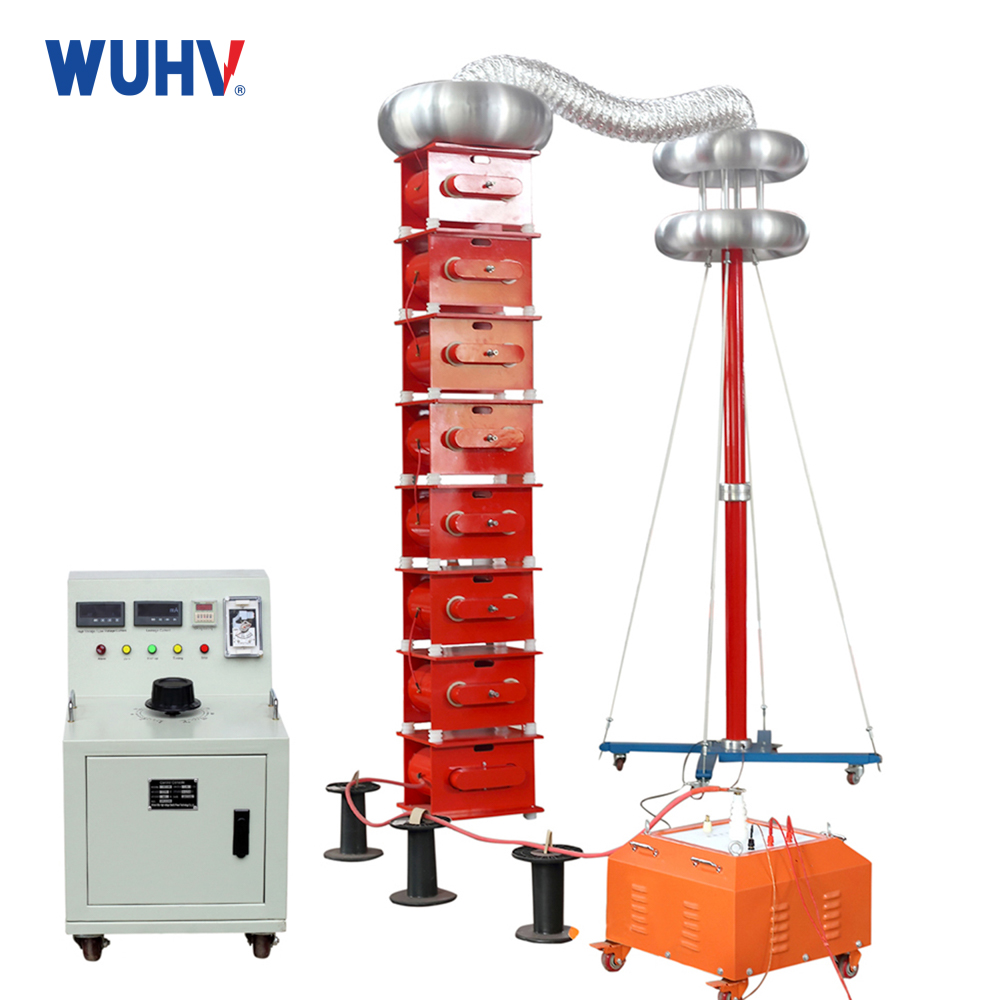
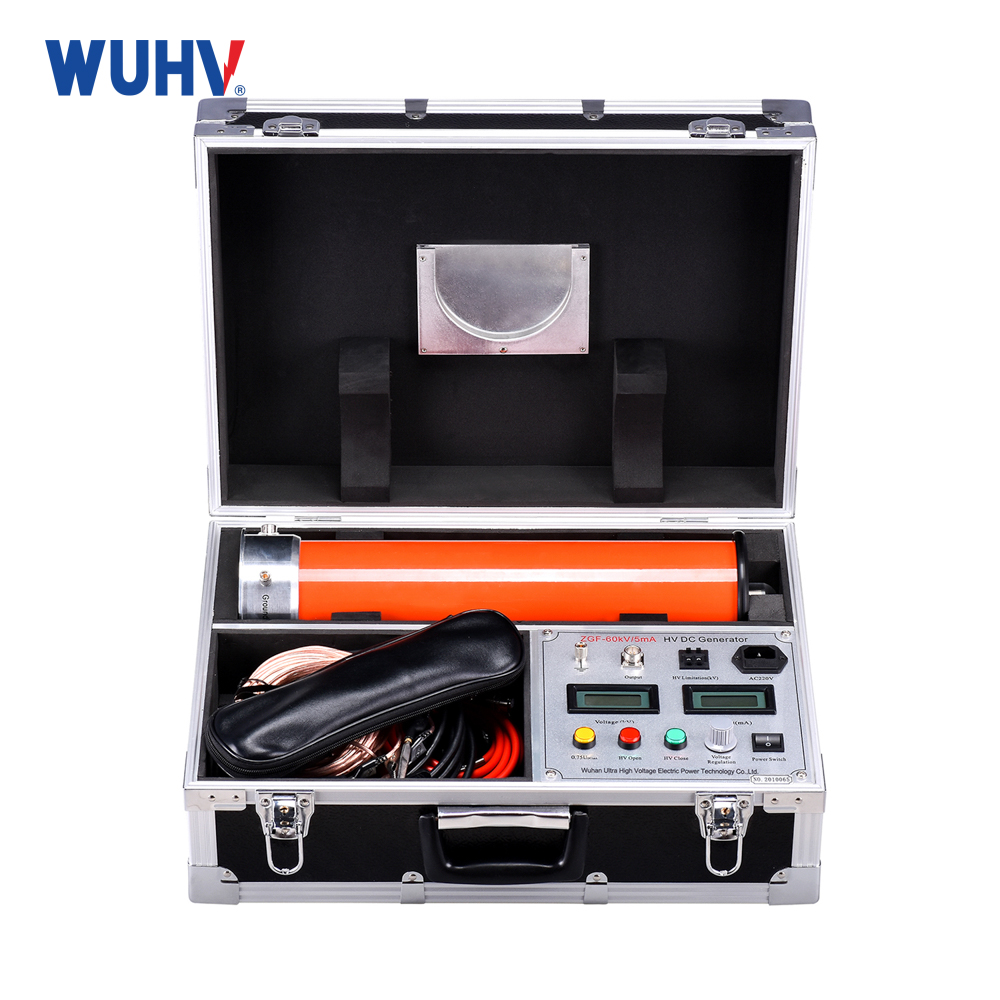
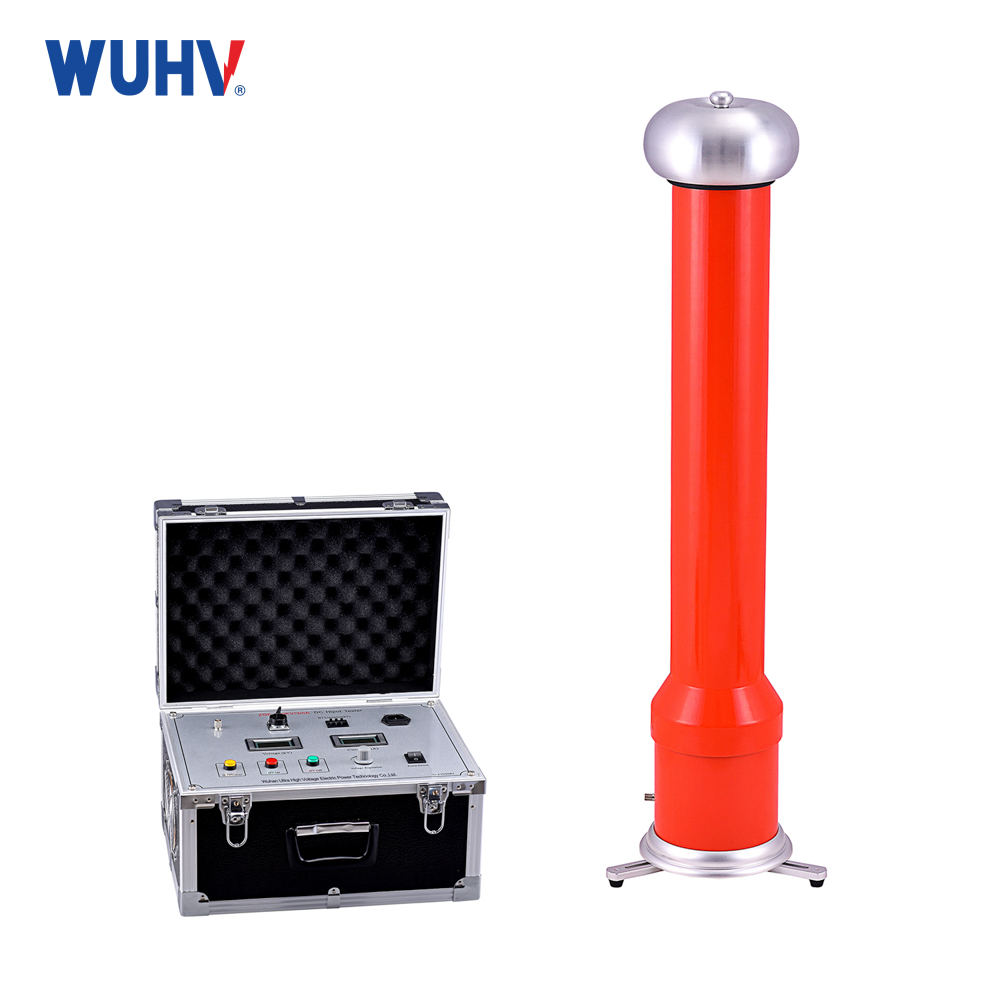
The DC hipot testKit under Wuhan UHV can help many power workers conduct various power tests more conveniently.
1.DC Hipot Test
Purpose:Verifies dielectric strength – the insulation’s ability to withstand high voltage without breaking down.
Method:Applies a destructively high DC voltage (e.g., 2× to 10× operating voltage) to the insulation.
Measurement:Monitors leakage current (µA/mA).
Outcome: Pass/Fail (fails if current exceeds threshold or breakdown occurs).
Risk:Potentially damages weak insulation. Critical safety step: Must discharge capacitive loads post-test.
Use Cases:
Safety certification (UL/IEC compliance).
Production line quality checks.
Detecting critical flaws (cracks, voids, thin spots).
2.Megger Test
Purpose:Measures insulation resistance – quantitative health of the insulation.
Method:Applies a safe, low-to-medium DC voltage (e.g., 500V, 1000V, 2500V).
Measurement:Reads resistance (MΩ/GΩ). Higher values = better insulation.
Outcome: Numeric value (e.g., "200 MΩ"), used for trend analysis.
Risk:Non-destructive; no discharge needed.
Use Cases:
Predictive maintenance (moisture, contamination, aging).
Troubleshooting insulation degradation.
Field inspections.
3.Core Contrasts
Voltage:
DC Hipot: High (stress test).
Megger: Low (diagnostic test).
Focus:
DC Hipot: "Will insulation survive a voltage surge?"
Megger: "How healthy is the insulation?"
Results:
DC Hipot: Binary (Pass/Fail).
Megger: Quantitative (resistance value).
Safety:
DC Hipot: Requires post-test discharge (lethal stored energy risk).
Megger: Safe for routine use.