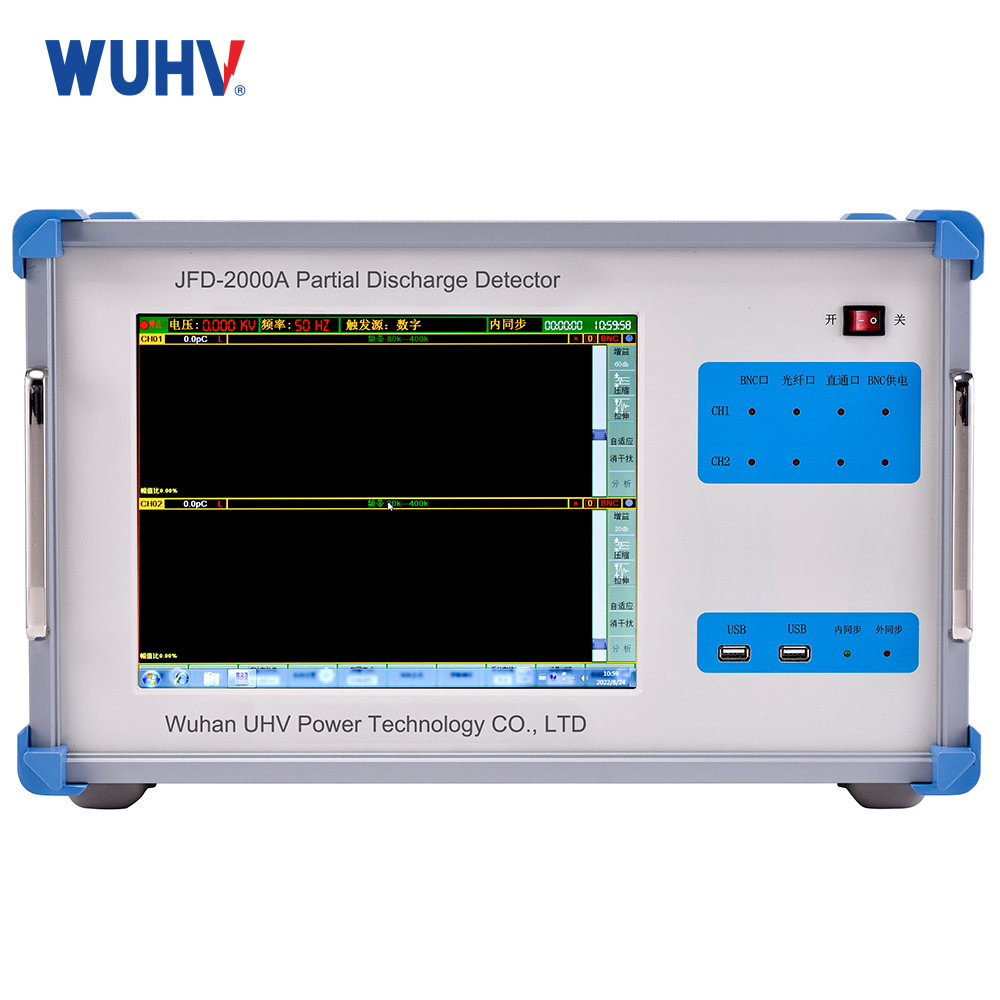
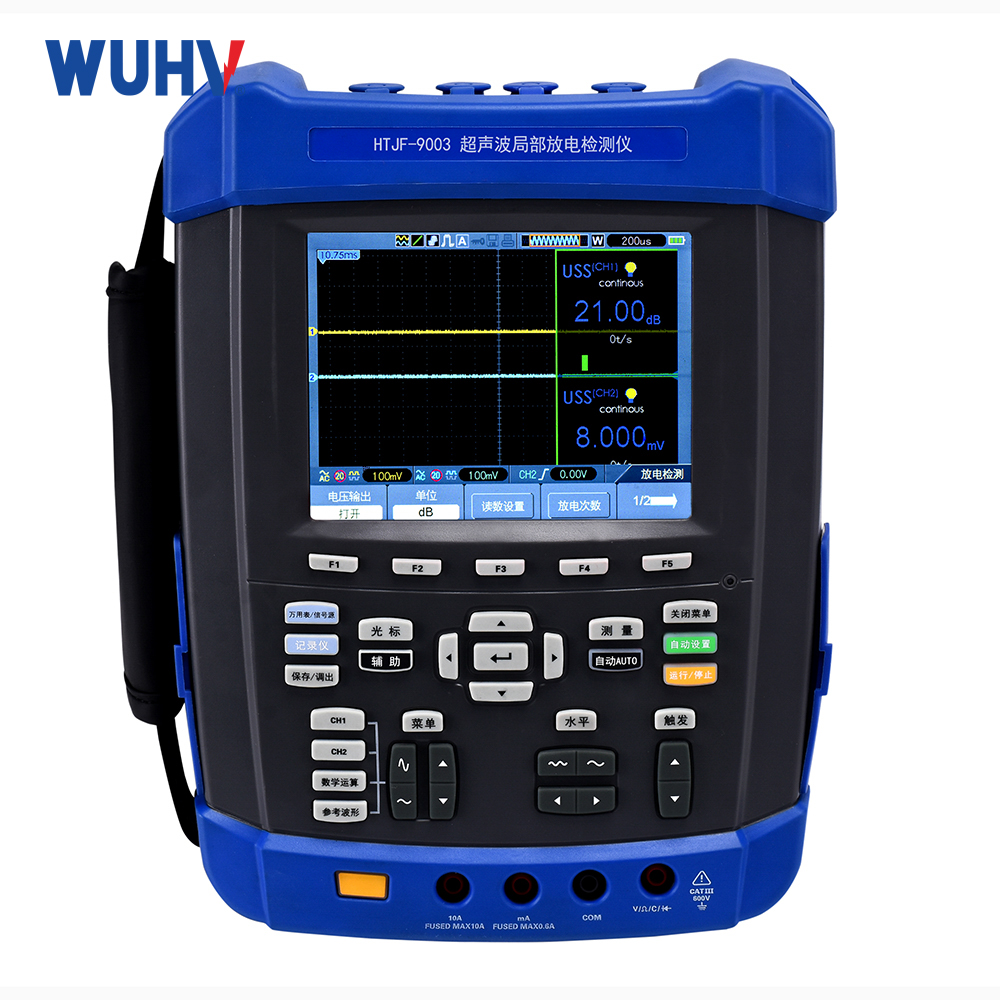
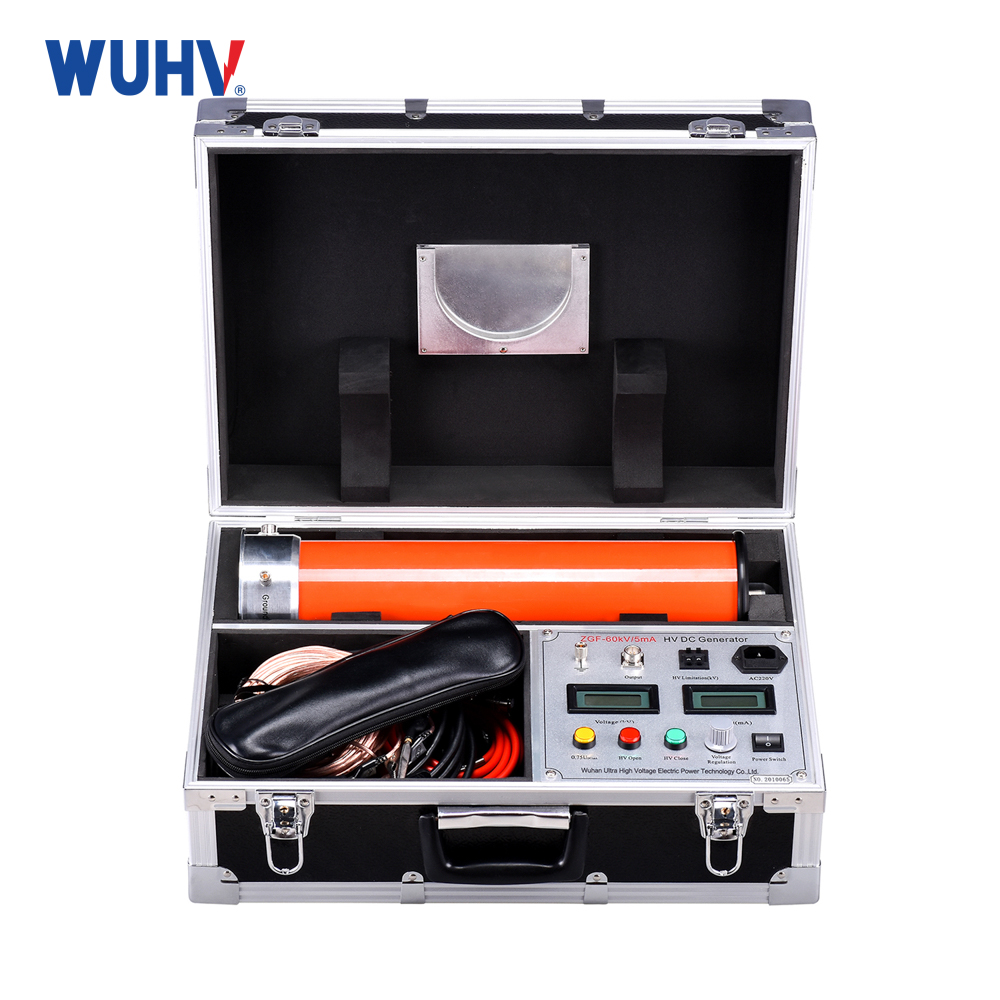
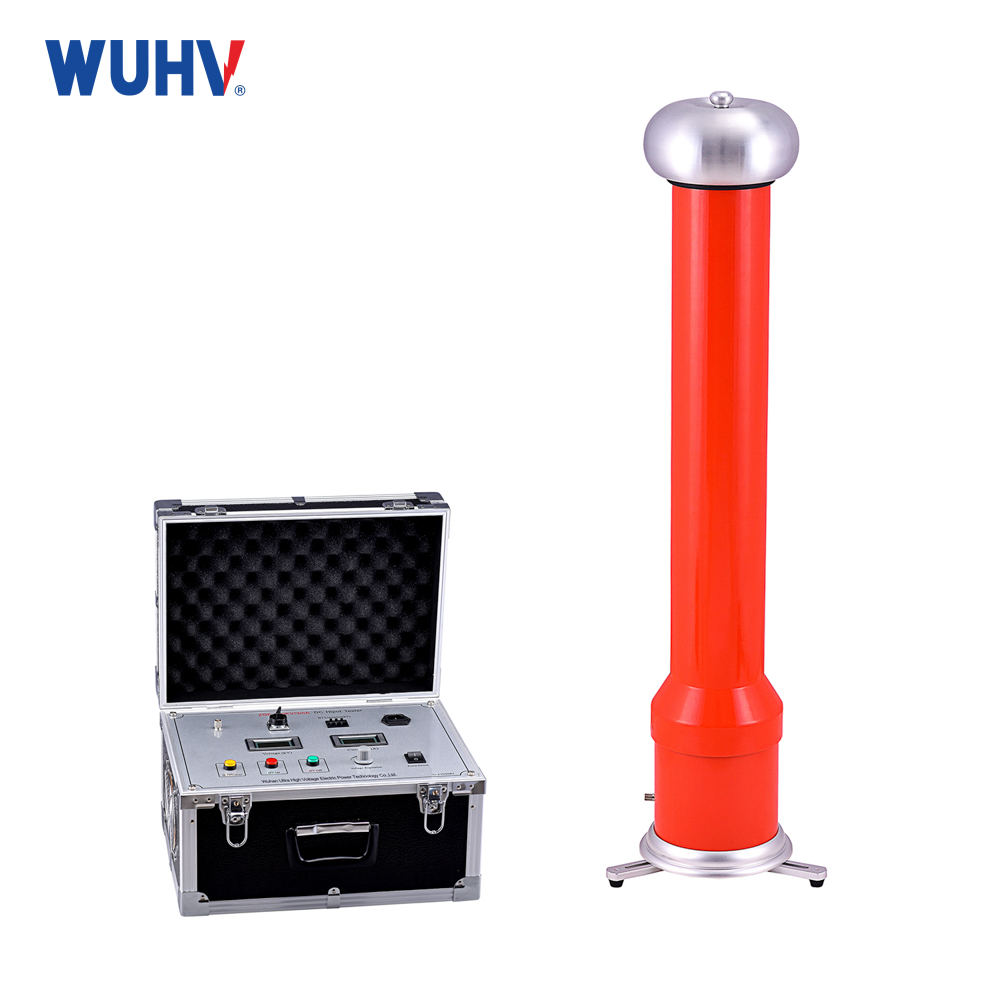
The DC resistance tester under UHV power can help many power workers conduct various power tests more conveniently.

The measurement of DC resistance is to check the welding quality of the winding and the short-circuit situation between the windings; Whether the position of the tap changer is good and whether the actual position is consistent with the indication; Whether the wire is broken or loose; And the winding of the strands did not break. Stocks and so on. The measurement of DC resistance is an essential inspection item for transformers after major repairs, pre tests, and changes in tap changer positions. It is also an important inspection item after faults.
In general, measuring the DC winding of transformer windings and high-power inductive devices using conventional methods (bridge method and voltage drop method) is a time-consuming and labor-intensive task. In order to change this situation, shorten measurement time, and reduce the workload of testers, Wuhan Hezhong Electric has developed a DC resistance rapid tester (hereinafter referred to as the DC resistance tester). It is an ideal choice for measuring transformer windings and DC resistance of high-power inductive devices.
Therefore, the measurement and testing of DC resistance must be handled with care to minimize measurement errors as much as possible. For transformers above 160kVA, the phase resistance difference is generally not greater than 2% of the average three-phase value. The resistance difference between wires generally does not exceed 1% of the average value of the three phases. For transformers of 160kVA and below, the difference in phase resistance is generally not greater than three. 4% of the average phase value, and the line deviation is generally not greater than 2% of the average three-phase value; The measured phase difference should not exceed 2% compared to the phase difference measured in the previous section.
When the resistance value measured by the DC resistor exceeds the standard:
1 . Firstly, consider whether there are measurement errors (such as whether the external leads are properly connected, whether the probes are too long or too thin, good contact, insufficient battery voltage on the bridge, etc.).
2 . The DC resistance value is greatly affected by temperature, so it must be converted to the same temperature (usually 20 ℃, R20=(T+20)/(T+t), T copper=235) for comparison. Generally, the above oil layer temperature is the basis.
3 . The currently used three-phase distribution transformer adopts a Y-shaped connection for the high-voltage winding. When the resistance exceeds the standard, the following equation [RA=(RAB+RAC-RAC)/2, RB=(RAB+RBC-RAC)/2, RC (RBC+RAC-RAB)/2] can also be used to find the defect stage.
4 . Poor contact of the tap changer causes the resistance value to increase. If the switch is not clean, the coating is not clean, the spring pressure is insufficient, the force is uneven, and there is carbon deposition on the overvoltage contact, the resistance will be high. At this point, the tap changer cover should be opened and rotated back and forth several times, which can generally be eliminated.
After the above inspection and processing, it still exceeds the standard, indicating an internal fault, which is likely due to soldering, desoldering, wire breakage, or interlayer short circuit between the winding and lead, or winding burnout. Unable to handle on-site, needs to be sent to the repair room for core repair.